The free movement of citizens is closely tied to their right to undergo training and engage in a professional activity. In this framework, having one’s experience and training recognized outside one’s country of origin may be required. In response to this highly topical issue – student mobility has risen by more than 30% in the last five years –, the ENIC-NARIC network (European Network of Information Centres – National Academic Recognition Information Centres) is committed to promoting abroad studies by ensuring the mutual recognition of diplomas and training earned within the European Union. Managed by the European Commission, the Council of Europe and UNESCO, and operating from 57 centers around Europe, it is the reference network and authority for the academic recognition of foreign diplomas. Beyond Europe’s borders, many organizations are committed to applying the same logic of harmonization to promote international mobility.
Find out what the international recognition of diplomas involves, the steps required to validate that credential and even the technology of micro credentials.
Why apply for the recognition of a diploma?
What is diploma recognition, and who issues it?
Diploma recognition, also called “statement of comparability”, is an official document issued by ENIC-NARIC in Europe, and by independent bodies outside Europe.

This certificate provides information about the validated diploma, such as:
- the exact title;
- the institution where the training was provided;
- the issue date;
- the duration of the training;
- the job leads and potential opportunities.
Diploma recognition was implemented to promote international mobility through a harmonized and streamlined reading of student backgrounds. How does it work? A foreign qualification is correlated with the various levels of the National Qualifications Framework and the European Qualifications Framework (EQF) – or with equivalent levels in the target country outside Europe – to guarantee mutual recognition of credentials and support professional integration as well as further studies. Recognition of qualifications is not compulsory, but may be requested by some employers, training centers or schools around the world.
However, a distinction should be made between “recognition” and “equivalence”. While an equivalence is more official, it involves much more stringent procedures and costs up to three times as much as diploma recognition certificates.
What is the purpose of the statement of comparability?
An application for diploma recognition can be made for different reasons:
- further study;
- seeking employment;
- naturalization application;
- engaging in regulated professions such as real estate agent;
How to obtain diploma recognition?
Statement of comparability for your diploma in Europe
Some schools in Europe only enroll students with a statement of comparability. To obtain diploma recognition in Europe, it is recommended to get in touch with a NARIC or ENIC center in the country of destination. The ENIC-RANIC.net website lists all such centers in Europe. If there isn’t one in the country in which you wish to apply for diploma recognition, pay a visit to your own country’s embassy, which will be able to guide you in obtaining the certificate.
If the student is involved in a mobility scheme organized within the European Union (such as the Erasmus program), recognition of diplomas is automatically included in the exchange agreements. In some cases, it is generated through the application of the European Credit Transfer System (ECTS). In such cases, the applicant will be exempted from applying for recognition.
Diploma recognition outside Europe
Outside the European zone, reference centers for the recognition of diplomas may differ from country to country:

- SEFRI or CDIP in Switzerland. It costs CHF 150 to obtain a statement of comparability.
- The Department for the Recognition of Diplomas in Luxembourg. Recognition costs between €75 and €300 depending on the document requested;
- Credential agencies in the U.S. The price for diploma recognition may vary, around $150 on average;
- Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) issues the ECA (Educational Credential Assessment) in Canada. The cost is approximately CA$ 200.
Similarly to ECTS (European Credits Transfer System) credits harmonized within member countries of the European Union, the American Academic Credits is a system used in the United States to harmonize American educational courses. For any request for equivalence, it is recommended to contact a Credentials organization – expecting high costs and relatively long delays.
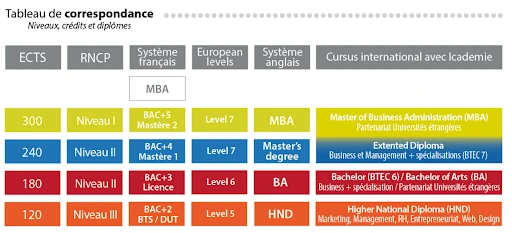
This table features all equivalences by level, credits and diploma, in and outside the European zone:
The issue with translating official documents
And then there’s the issue of translating foreign diplomas. Although translation is a great way to make the information accessible to the country receiving the diploma recognition application, it can prove misleading. Some terms do not have an equivalent in the target language, which can be a source of misunderstanding. The level of the diploma may therefore be incorrect. In general, official translations from foreign institutions or sworn translators (in the applicant’s country of origin) are accepted, but this is not the case for all organizations. Be sure to check to what extent and under what conditions a translation is needed.
If the diploma obtained abroad matches or is equivalent to a certification or diploma in the target country, a statement of comparability will be sent to the applicant.
BCdiploma’s solution for storing your diploma recognition
Dematerialization is on the rise, and statements of comparability for diplomas are no exception. In this field, more and more blockchain solutions have emerged, allowing graduates to store all their learning outcomes (certificates, diplomas or digital open badges) in one single dedicated space. In the era of digitization of credentials, the ENIC-NARIC center has decided to partner with BCdiploma and its blockchain solution to digitize its statements of comparability. Secure, forgery-proof and GDPR-compliant, blockchain is the technology of the future for data processing.
